Palladium recovery: Retrieve your precious metal before it is lost
Identify and specifically avoid gold losses
- Concentration losses in process baths through repeated use
- Palladium residues in rinse water after coating
- Sludges and filter residues with bound precious metal
- Fine palladium particles in exhaust air, settling on surfaces
Electrolytic palladium recovery: Maximum precious metal yield from liquid media
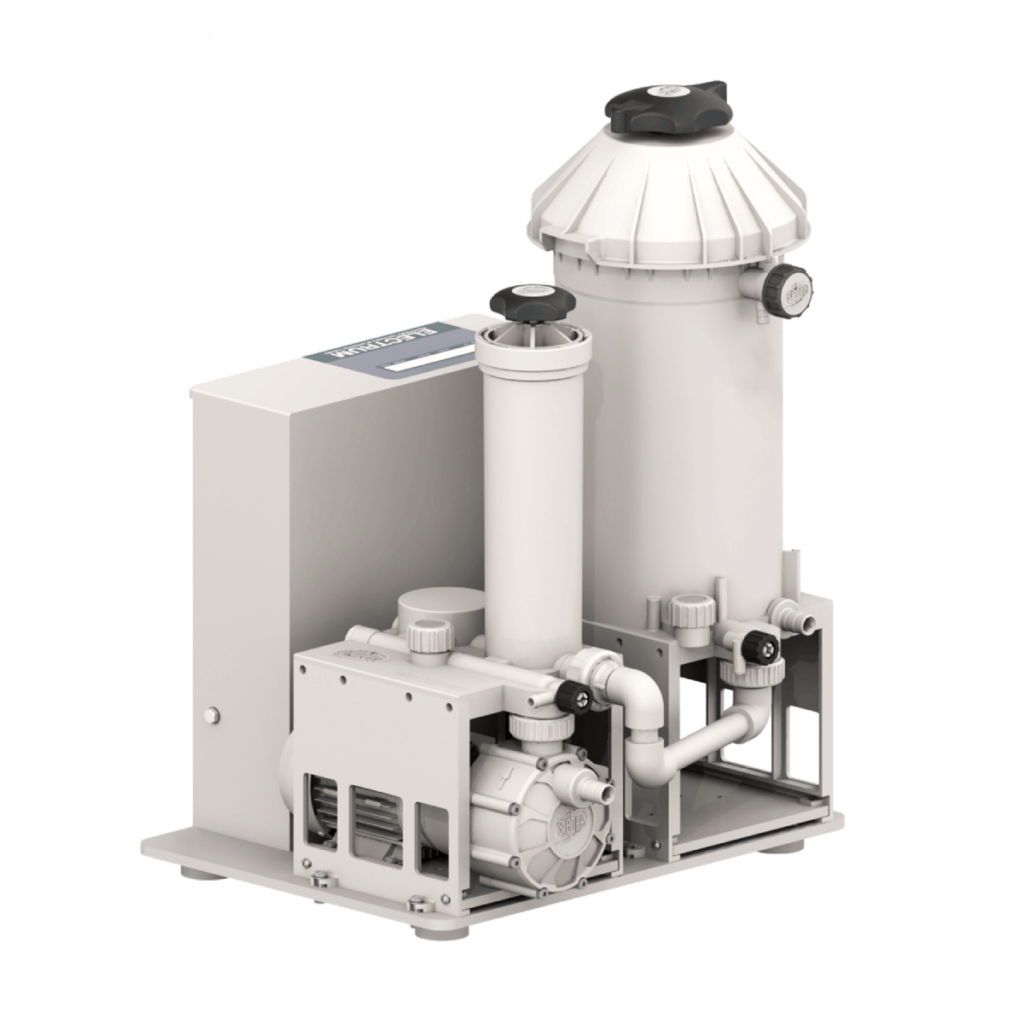

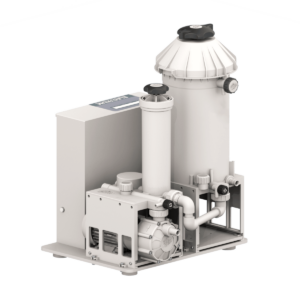
How electrolytic recovery works in detail
Electrolytic recovery uses controlled direct current to deposit palladium directly from the liquid. The entire process runs in several clearly defined steps:
- Fluid introduction: The palladium-containing process liquid is directed into the reactor of the facility.
- Current introduction: A defined direct current is generated between an anode and a cathode. This electrically charges the palladium ions in the liquid.
- Migration of palladium ions: The positively charged palladium ions move specifically towards the negatively charged cathode through the electric field.
- Deposition of palladium: At the cathode surface, the palladium deposits in a solid, metallic form.
- Metal removal: After the process is completed, the cathode can simply be removed. The deposited palladium can then be further processed and rewarded after forwarding to the refinery/recycler.
Thanks to the precise control of current strength, voltage, and flow rate, the entire process can be optimally adapted to the respective palladium concentration and throughput.
Technical specifications of the Electrum system
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum current strength | 30 Amperes |
| Maximum voltage | 12 Volts |
| Throughput capacity | Up to 3 m³ per hour |
| Electrode material | Titanium with precious metal coating |
| Reactor material | Polypropylene or PVDF (chemical resistant) |
| Control | Electronic regulation with display |
| Operating temperature | 10 to 60 degrees Celsius |
| Protective functions | Overcurrent protection, temperature sensors, leakage control |
| Connection voltage | 230 Volts or 400 Volts depending on the system type |
| Installation space | Approx. 1.5 square meters (depending on the model) |
Features and particularities
- High separation performance: Even low palladium concentrations are reliably separated.
- Compact design: Minimal space requirement for flexible integration into existing systems.
- Energy-efficient operation: Optimized current flow reduces operational costs permanently.
- Robust materials: All parts in contact with media are made of chemical-resistant materials.
- Safety features: Integrated overcurrent protection and leakage control systems ensure safe operation.
- Maintenance-friendly design: All relevant components are easily accessible for quick cleaning or maintenance.
How to save real money with palladium recovery
Improved process safety and consistent product quality
A consistent palladium content in your process baths is crucial for consistently high product quality. Fluctuating precious metal concentrations often lead to problems in coating or electroplating. Typical consequences include adhesion issues, uneven layer thicknesses, or rejects.
With electrolytic palladium recovery, you stabilize the bath composition in the long term. This reduces quality defects and lowers the rate of defective parts. At the same time, the maintenance effort for your systems decreases as fewer residues deposit in the system.
Typical applications for palladium recovery
- Electroplating companies: Palladium primarily enters the waste stream through rinse waters and process baths. Recovery keeps the precious metal in circulation, significantly reducing operational costs.
- Electronics manufacturing: Palladium coatings are often used in the production of circuit boards or connectors. Recovery reduces material losses and ensures stable production conditions.
- Chemical industry: In catalytic processes with palladium-containing solutions, large amounts of material can be recovered. This reduces raw material consumption and improves the plant’s economic efficiency.
- Recycling companies: Companies that process precious metal-containing waste benefit from electrolytic recovery to specifically reclaim the precious metal content from aqueous media.
- Research institutions: Even in laboratories and pilot plants, where expensive precious metals are often used, recovery pays off through reduced material costs and lower waste.
Contact
Would you like to learn more about how much palladium you are currently losing unnoticed? Or would you like to request a custom offer for electrolytic palladium recovery directly?
Then get in touch with us now. Our experts provide personal advice, analyze your situation, and develop a tailor-made solution for your operation.

